Tag: m247
-

IVPN
App Telemetry In our analysis, IVPN primarily establishes connections to its own domain, api.ivpn.net, which can be logically tied to the app’s core functionality. A notable feature is its lack of telemetry, reinforcing its standing as a true privacy-focused application. Additional connections to Apple’s ecosystem, namely inappcheck.itunes.apple.com and mzstorekit.itunes.apple.com, are indicative of routine in-app functionality…
-

Windscribe
Windscribe, a cross-platform virtual private network (VPN) service provider, was founded by Yegor Sak and Alex Paguis in 2016. Based in Canada, it has grown to operate internationally, supporting a broad range of operating systems and platforms, and providing services to personal computers, smartphones, routers, and smart TVs1. The company’s offerings include OpenVPN, Internet Key…
-

Surfshark
Surfshark VPN is one of the most popular VPN services in 2022. Its competitive price and unlimited simultaneous connections make it a very attractive VPN option for all kinds of users. But does this VPN live up to give the actual value for money that it claims? Surfshark also offers thousands of servers worldwide, excellent…
-

ProtonVPN
ProtonVPN is a virtual private network (VPN) service provided by Proton Technologies AG, the company behind the email service ProtonMail. ProtonVPN was created to provide a secure, private, and censorship-free internet connection to people all over the world. It encrypts your internet connection and hides your IP address, making it difficult for hackers, ISPs, and…
-

AdGuard VPN
AdGuard has offered ad-blocking and tracking protection software for over 10 years, so my expectations of its VPN were reasonably high. On AdGuard’s website, there are several promises. It boasts about providing you with high speeds, the ability to virtually teleport you around the world, and keep you safe online. It also promises you the…
-

CyberGhost VPN
CyberGhost VPN was founded in 2011 in Bucharest, Romania, and initially began as a free VPN service. By the following year, it had gathered around 1.7 million users. In 2017, a notable change occurred when Kape Technologies (then known as Crossrider) acquired CyberGhost VPN. This acquisition brought about concerns among observers due to Crossrider’s background…
-

Aloha Browser VPN
The Aloha Browser is one of the up-and-coming new browser apps for mobiles which targets one of the most important aspects of modern browsing — privacy. The Aloha Browser is the only browser (to our knowledge) that comes with a built-in VPN and encrypts user data at all levels. When you are using Aloha VPN…
-

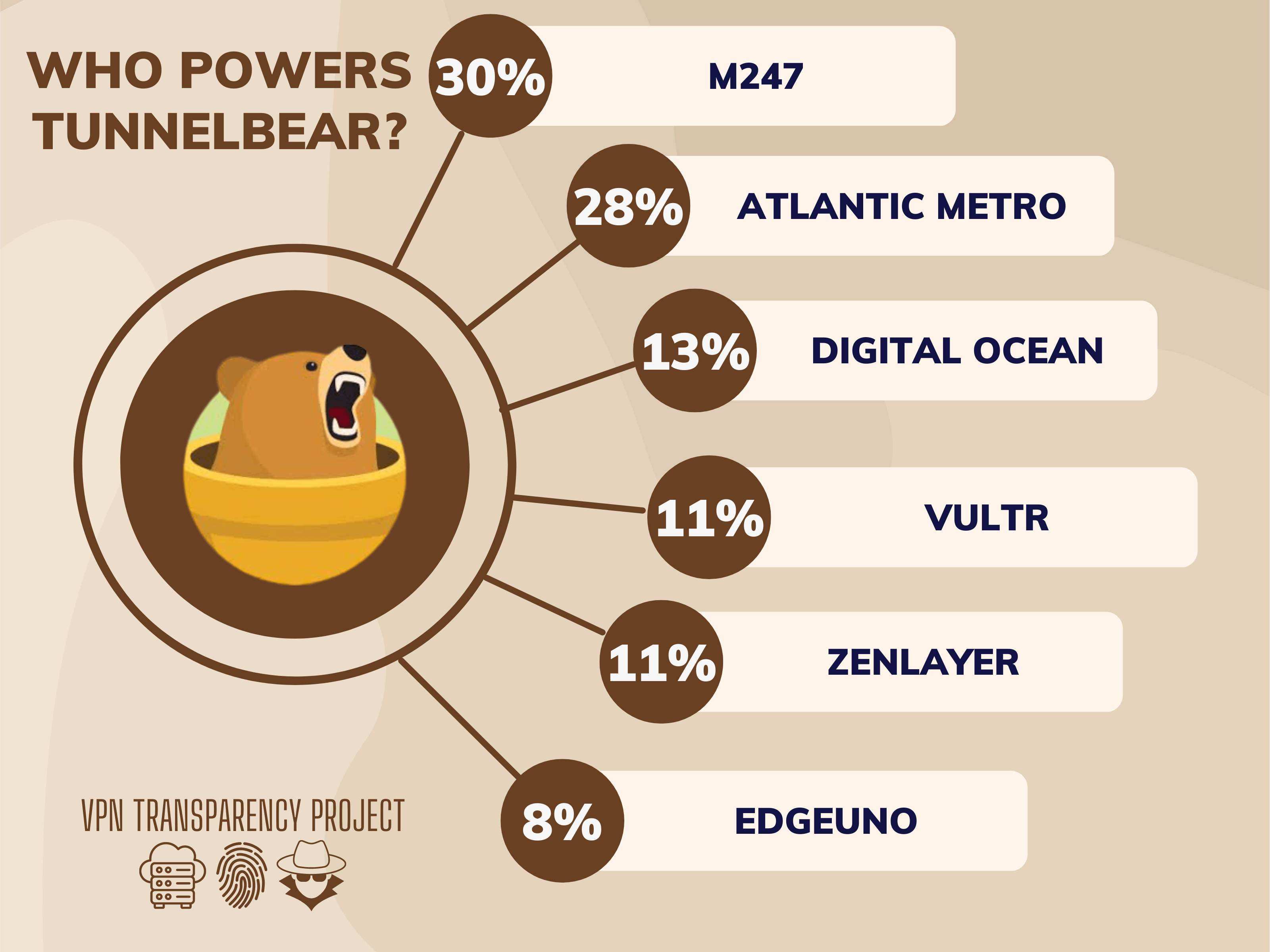
TunnelBear
TunnelBear is a virtual private network (VPN) service that is known for its user-friendly interface and its commitment to privacy and security. The company was founded in 2011 and is headquartered in Toronto, Canada. TunnelBear offers a range of VPN services that are designed to protect users’ online privacy and security by encrypting their internet…
-

VPN – Super Unlimited
Just about everyone knows what a VPN is these days, or at the very least, they’ve heard of them. And businesses keen on making a quick dollar have caught on to the recent surge in VPN users. A quick glance at the iOS App Store shows over a dozen VPN apps, all with their own…
-

Private Internet Access
Table of Contents Privacy Policy Terms of Service Log Policy Torrenting Use of virtual servers ASN Diversity Private Internet Access (commonly known as PIA) is a capable VPN provider, now owned by Kape, which also owns CyberGhost, ZenMate and ExpressVPN. PIA has servers available in just about every single state in America, which is great…