Tag: security
-

Protect Your Home: Prevention, Detection, Defense
When it comes to ensuring the safety and security of your home, a multi-tiered approach is essential. By layering preventive measures, detection systems, and last-resort defense options, you can create a robust security strategy that not only deters potential intruders but also provides peace of mind for you and your family. From physical barriers like…
-

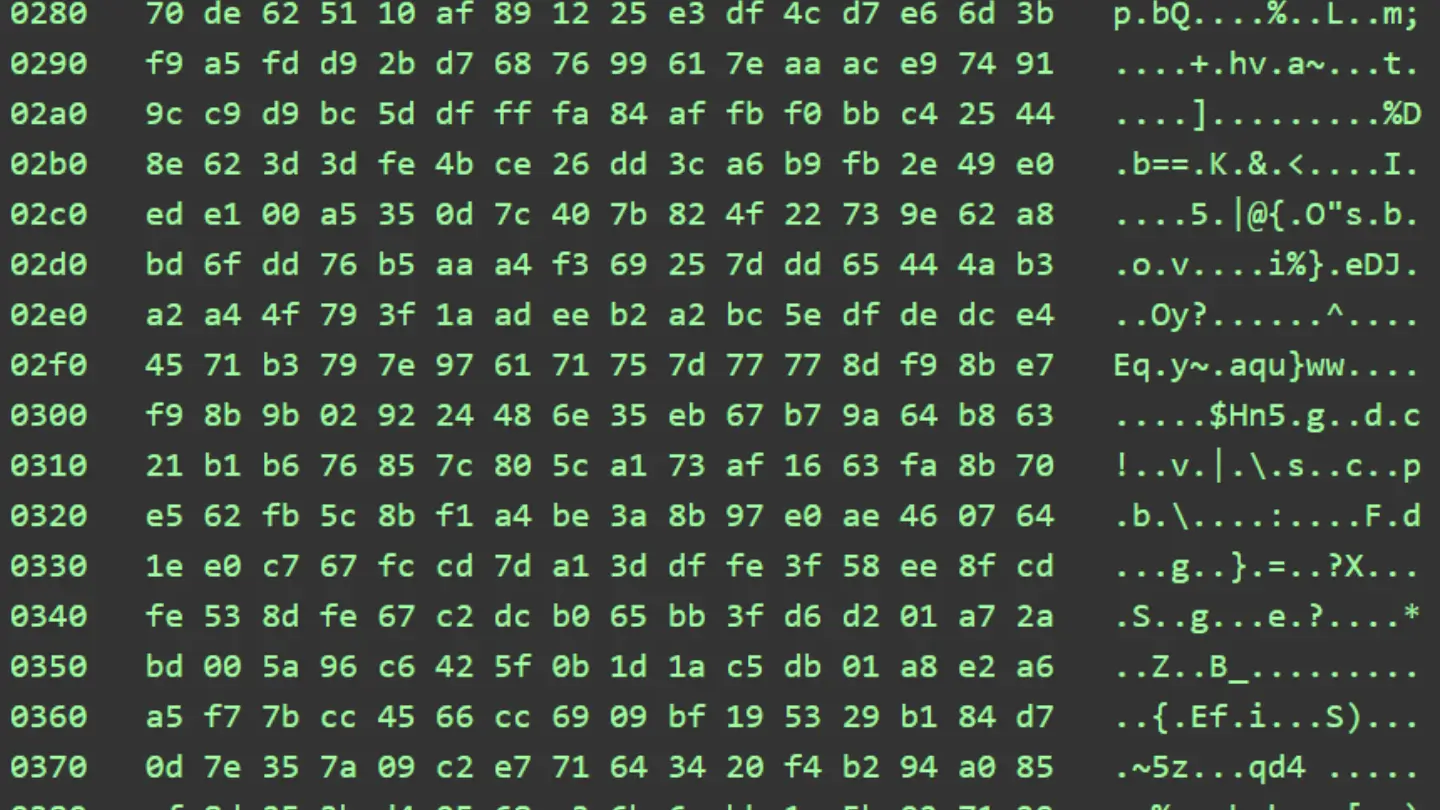
Reading Between the Bytes: Understanding Binary Data with Hex Dumps
Table of Contents Understanding the Structure of a Hexdump Reading and Interpreting Hexdumps Analyzing HTTP Traffic Understanding the Security Implications of Unencrypted HTTP Traffic Common Tools for Generating Hexdumps Practical Applications of Hexdumps Conclusion: The Pivotal Role of Hexdump Analysis in Digital Security As the digital landscape continues to expand and evolve, the tools and…
-

Cover Your Tracks: How to Delete Files Beyond Recovery
In today’s digital age, maintaining your privacy involves more than just safeguarding passwords and personal data. An often overlooked aspect is the secure deletion of files from your hard drive. Whether you’re a privacy-conscious individual, a professional dealing with sensitive data, or someone who simply wants to understand how to better manage their digital footprint,…
-

Mullvad VPN to Remove Port Forwarding Feature, Citing Security Concerns
In a move that has drawn attention from the cybersecurity community, Mullvad VPN, a popular provider known for its commitment to privacy, has announced it is discontinuing support for port forwarding. The company cites frequent misuse of this feature, leading to negative experiences for the majority of its users, and more troublingly, garnering unwanted attention…